
The electric field is visualized as logarithmically scaled arrows. The electric potential is visualized as filled contours with labels indicating the potential level. In certain cases, the volume charge density can also be an output of the analysis.Ī cross-sectional view of the electric potential and field throughout the volume surrounding a parallel plate capacitor. Note that for an electrostatics analysis, there is no current input or output due to the fact that all charges are considered stationary. Typical inputs and outputs for an electrostatics analysis are summarized below: Inputs When performing an electrostatics analysis, any conducting materials, typically metals, are first removed from the analysis, and the metallic surfaces are seen as exterior boundaries from the perspective of the dielectric materials. As an approximation of Maxwell's equations, electrostatics can only be used to describe insulating, or dielectric, materials entirely characterized by the electric permittivity, sometimes referred to as the dielectric constant. ElectrostaticsĮlectrostatics is the subfield of electromagnetics describing an electric field due to static (nonmoving) charges. Instead, a more practical understanding of electromagnetics comes from considering a number of special cases, including electrostatics, steady currents, magnetostatics, quasistatic alternating currents, inductive phenomena, microwave engineering, and optics. In real-world applications, it is rarely necessary to consider all possible electromagnetic phenomena that may occur. The meaning of these equations is described in the sections and subsections below.

Maxwell's equations are listed in the table below in their differential form: Equation Name In engineering applications, these equations almost always need to be supplemented by additional laws related to how electromagnetic fields interact with media.
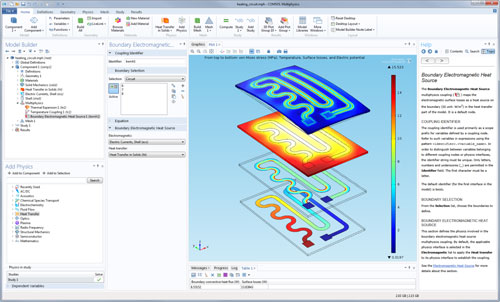
Despite their widely differing characteristics, all of these application areas are fundamentally described by Maxwell's equations. A device used in an electrostatics setting, such as a capacitor, may have very little in common with one from optics, such as an optical fiber.
Electromagnetics What Is Electromagnetics?Īs an engineering field, electromagnetics is traditionally approached through the jargon and devices belonging to one of many subfields, such as electrostatics or optics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
